Certain drugs can increase the risk of falling. This is a concern for many, especially the elderly.
Understanding which medications contribute to this risk is crucial for safety. Falls are a leading cause of injury, particularly among older adults. Medications play a significant role in these incidents. Some drugs affect balance, coordination, or awareness, making falls more likely.
Doctors and patients need to be aware of these risks. Knowing which medications have these side effects can help prevent accidents. It's important for everyone, especially those caring for seniors, to be informed. This knowledge enables better management of medication use. In this blog, we will explore the drugs that can increase the risk of falling. We'll discuss how they affect the body and what precautions can be taken. Stay informed and help reduce fall-related injuries.
Common Medications
Every year, countless individuals experience falls that can lead to serious injuries. While many factors contribute to these incidents, medications play a significant role. Certain drugs can increase the risk of falling. Understanding which common medications pose this threat is crucial for prevention. This knowledge helps patients and caregivers make informed decisions about health and safety.
Professional Fall Prevention Home Care in Houston, TX - Visit Us Today
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are widely prescribed for managing depression and anxiety. These medications affect neurotransmitters in the brain, helping to balance mood. Yet, they can also influence physical stability. Some common side effects include dizziness, sedation, and impaired coordination. These symptoms increase the likelihood of falls, especially in older adults.
Here's a closer look at how antidepressants contribute to fall risks:
Dizziness: Sudden movements can cause lightheadedness, leading to loss of balance.
Sedation: Feeling overly relaxed or sleepy might delay reaction times.
Coordination issues: Difficulty in movement can result in stumbling or tripping.
Different classes of antidepressants have varying impacts. For instance:
Type | Impact |
SSRIs | May cause dizziness and sleep disturbances. |
Tricyclics | Often lead to sedation and blurred vision. |
Patients should regularly consult their healthcare providers. Adjustments in dosage or switching medications can reduce fall risks.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are primarily used for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. They work by calming the nervous system. Yet, this calming effect can have unintended consequences. Users might experience drowsiness, muscle weakness, and decreased alertness. These factors contribute significantly to fall incidents.
Common benzodiazepines include:
Diazepam
Lorazepam
Clonazepam
How do benzodiazepines increase fall risks?
Drowsiness: Makes it difficult to stay alert, especially in unfamiliar surroundings.
Muscle relaxation: Can lead to weak muscles, impacting stability.
Impaired judgment: Reduces ability to assess safe movements.
It's vital for users to monitor their reactions to these drugs. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help manage side effects. Discussing alternatives or non-drug therapies may also be beneficial.
Blood Pressure Drugs
Falling can be a serious issue, especially for older adults. Certain medications can increase this risk. Blood pressure drugs are among them. They are crucial for managing high blood pressure. Yet, they can also lead to dizziness or lightheadedness. This can make a person more likely to fall. Understanding which drugs affect balance can help in taking precautions. Let’s explore two common types of blood pressure medications: Diuretics and Beta-blockers.
Diuretics
Diuretics, also known as water pills, help the body get rid of extra salt and water. They are effective in lowering blood pressure. But they can also cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. These side effects can increase the risk of falls.
Dizziness: Losing too much water can make you feel dizzy.
Weakness: An imbalance in electrolytes can lead to muscle weakness.
Frequent urination: This can cause urgency and increase the chance of slipping.
Here’s a quick look at some common diuretics:
Diuretic Name | Common Side Effect |
Furosemide (Lasix) | Dizziness |
Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) | Fatigue |
Spironolactone (Aldactone) | Muscle cramps |
To reduce the risk of falling, it’s important to stay hydrated. Have regular blood tests to check electrolyte levels. This can help manage side effects effectively.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers slow down the heart rate. They help lower blood pressure by reducing the workload on the heart. While effective, they can cause side effects that may lead to falls.
Some common issues include:
Slow heart rate: Can cause dizziness or fainting spells.
Fatigue: May affect balance and coordination.
Cold extremities: Numbness in feet can lead to tripping.
Here is a list of popular beta-blockers and their potential side effects:
Beta-blocker Name | Common Side Effect |
Atenolol (Tenormin) | Cold hands and feet |
Metoprolol (Lopressor) | Drowsiness |
Propranolol (Inderal) | Lightheadedness |
Monitoring your heart rate regularly can help in managing these side effects. Consider discussing any concerns with your healthcare provider. This can help in adjusting dosages or switching medications if needed.
Pain Management Medications
Managing pain is crucial for many people. But some medications can make falling more likely. Falls can be dangerous. Especially for older adults. It's essential to know which drugs might increase this risk. Pain management medications are common. They help with chronic pain. Yet, some of these drugs can lead to dizziness or drowsiness. This might make balance harder. Knowing which medicines can cause falls is important. It helps in making safer choices.
Opioids
Opioids are strong painkillers. They are used for severe pain. Often after surgery or injury. But they have side effects. These can increase the risk of falling. Opioids can cause:
Drowsiness: This can make you sleepy and less alert.
Dizziness: Feeling unsteady or lightheaded.
Impaired coordination: Hard to move safely.
These effects can make walking difficult. Balance might be harder to maintain. The risk of falling increases, especially for older adults. Opioids can also slow reaction times. This makes it hard to catch yourself if you start to fall. If you use opioids, be cautious. Talk to your doctor. They might adjust your dose. Or suggest alternatives. Safety is important.
Nsaids
NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They help with pain and inflammation. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen and aspirin. They are often used for arthritis or minor injuries. NSAIDs have fewer side effects than opioids. But they are not without risk. They can cause:
Stomach upset: Leading to discomfort and distraction.
Increased bleeding risk: This can be dangerous if you fall.
Though NSAIDs don't cause dizziness like opioids, they can still increase fall risk. Especially if they lead to gastrointestinal issues. It's important to take NSAIDs as directed. Avoid taking them on an empty stomach. This helps prevent stomach problems. If you have a history of falls, talk to your healthcare provider. They might recommend safer pain management options. Always prioritize safety when managing pain.
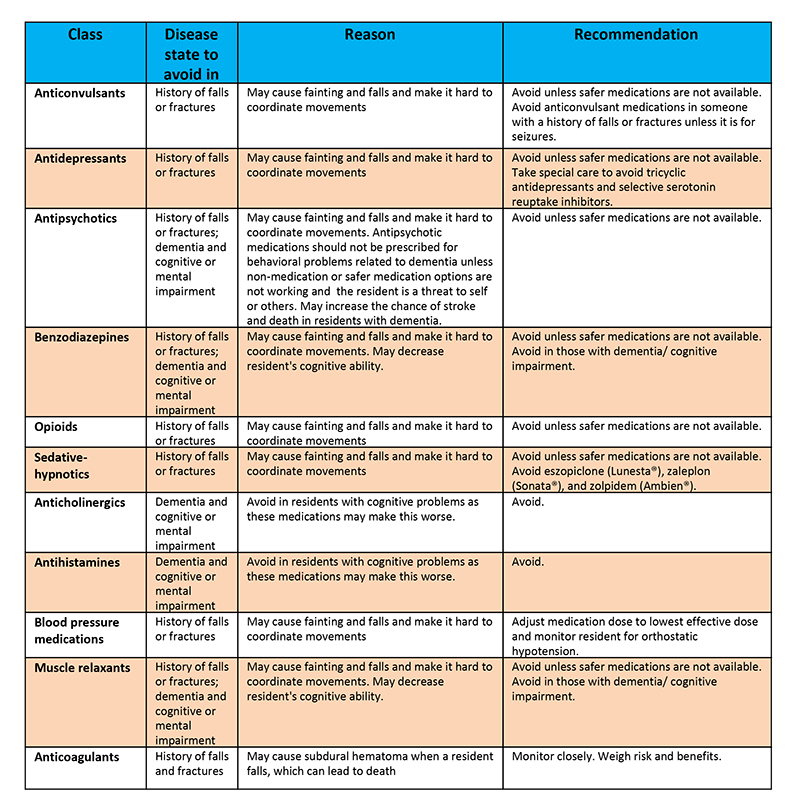
Sedatives And Sleep Aids
Falls are a major concern for people, especially as they age. Various factors contribute to this risk, including certain medications. Sedatives and sleep aids, widely prescribed for insomnia and anxiety, can significantly impact balance and coordination. These drugs often cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired motor skills, making individuals more prone to falls. Understanding which medications increase fall risk can help prevent accidents and promote safer living conditions.
Z-drugs
Z-drugs, including zolpidem, zaleplon, and eszopiclone, are commonly used to treat sleep disorders. Though effective in promoting sleep, they come with potential side effects. Their sedative properties can lead to dizziness and reduced alertness.
Dizziness: A common side effect that affects balance.
Next-day drowsiness: Impairs daily activities.
Memory issues: Can cause confusion and disorientation.
The table below highlights some key points about Z-drugs:
Drug Name | Common Side Effects | Risk of Falling |
Zolpidem | Dizziness, headache | High |
Zaleplon | Short-term memory loss | Moderate |
Eszopiclone | Next-day drowsiness | High |
Monitoring these side effects is crucial. People taking Z-drugs should be cautious and consider discussing with healthcare professionals about alternative treatments.
Barbiturates
Barbiturates, once a popular choice for treating anxiety and sleep disorders, are now less commonly used. They include drugs like phenobarbital and secobarbital. Barbiturates work by depressing the central nervous system, which can cause significant sedation and muscle relaxation.
Key side effects include:
Severe sedation: Reduces alertness significantly.
Muscle weakness: Can lead to instability.
Dizziness and confusion: Increases fall risk.
Barbiturates also have a narrow therapeutic index, making the risk of overdose higher. This adds to the danger of falls. The table below provides an overview:
Drug Name | Common Side Effects | Risk of Falling |
Phenobarbital | Drowsiness, dizziness | High |
Secobarbital | Confusion, sedation | Very High |
For those prescribed barbiturates, regular monitoring and consultations with healthcare providers are vital. This ensures safety and minimizes the risk of falls.
Professional Fall Prevention Home Care in Houston, TX - Visit Us Today
Antipsychotics
Antipsychotics are medications used to treat severe mental health conditions like schizophrenia. They help manage symptoms like hallucinations and delusions. While effective, they can increase the risk of falls. This risk is particularly high among older adults. Understanding how these drugs contribute to falling is crucial for safety.
First-generation
First-generation antipsychotics are also known as typical antipsychotics. They are the older class of antipsychotic drugs. These medications can cause side effects that contribute to falls. Muscle stiffness and tremors are common. These can make walking difficult.
Chlorpromazine: Often leads to dizziness and impaired balance.
Haloperidol: Known for causing muscle rigidity.
Fluphenazine: Can lead to sedation, affecting alertness.
Studies show that these drugs can slow down reaction times. This delay can be dangerous when navigating obstacles. Older patients are particularly vulnerable. Their bodies may not compensate for these effects as well.
Below is a table summarizing some effects:
Medication | Common Side Effects |
Chlorpromazine | Dizziness, impaired balance |
Haloperidol | Muscle rigidity |
Fluphenazine | Sedation, decreased alertness |
Second-generation
Second-generation antipsychotics are often called atypical antipsychotics. They are newer and generally have fewer side effects. Yet, they still pose risks for falls. These drugs can cause dizziness and weight gain. Both increase the chance of falling.
Risperidone: May lead to low blood pressure, causing dizziness.
Olanzapine: Known for significant weight gain, affecting mobility.
Quetiapine: Can cause sedation, reducing alertness.
These drugs might affect balance by altering brain chemistry. Sedation and dizziness are common. Patients may feel off-balance or unsteady.
The following table shows some key side effects:
Medication | Common Side Effects |
Risperidone | Low blood pressure, dizziness |
Olanzapine | Weight gain, reduced mobility |
Quetiapine | Sedation, decreased alertness |
Being aware of these effects can help manage the risk of falling. Adjusting the medication dosage or using supportive devices can be beneficial. Regular check-ups are advised to monitor any changes in mobility or balance.
Muscle Relaxants
As we age, the risk of falling increases, especially when certain drugs are involved. Among these, muscle relaxants play a significant role. They are often prescribed to ease muscle tension and pain. But they can also impact balance and coordination. Understanding how these drugs work and their side effects can help in minimizing fall risks. Let's explore two common muscle relaxants: Cyclobenzaprine and Baclofen.
Cyclobenzaprine
Cyclobenzaprine is a widely used muscle relaxant. It helps relieve muscle spasms and pain. But it can also increase the risk of falls. This drug affects the central nervous system. It makes the brain feel relaxed and less aware of its surroundings.
Common side effects of Cyclobenzaprine include:
Drowsiness
Dizziness
Blurred vision
Dry mouth
These effects can lead to balance issues. Particularly in older adults. It is crucial to be cautious when using this medication.
Here is a simple comparison table to understand its effects:
Effect | Impact |
Drowsiness | Increases risk of falling |
Dizziness | Affects balance |
Always consult a doctor. Especially if you experience unusual symptoms. And avoid activities requiring alertness. Such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
Baclofen
Baclofen is another muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasms. It is effective in managing symptoms related to multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries. Yet, it has its own set of side effects that can elevate fall risks.
Key side effects include:
Weakness
Fatigue
Confusion
Nausea
These side effects can cause coordination problems. Making falls more likely. Especially in those who are already at risk.
Consider the following list of precautions:
Start with a low dose. Increase gradually.
Monitor for side effects regularly.
Report any severe symptoms to a healthcare provider.
Maintaining a safe environment is also crucial. Remove tripping hazards at home. Use assistive devices if necessary. These steps can help reduce the risk of falls when using Baclofen.
Antihistamines
Falls are a significant health concern, especially for older adults. Certain medications can increase this risk. Among these, antihistamines are notable. These are drugs commonly used to treat allergies. They can cause side effects that may lead to falls. Understanding how antihistamines affect balance and coordination is crucial. This knowledge can help minimize risks and ensure safety.
First-generation
First-generation antihistamines are well-known for their effectiveness in treating allergy symptoms. However, they come with a set of side effects. These drugs often cause drowsiness and sedation. This can lead to a higher risk of falls, especially in older adults. Here are some common first-generation antihistamines:
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton)
Brompheniramine (Dimetapp)
The sedative effects of these drugs can impair balance. This increases the likelihood of losing footing. They can also affect coordination and reaction time. This makes it harder to avoid obstacles. Older adults are particularly at risk. Their bodies process medications differently. This can lead to prolonged effects.
Here's a table summarizing the side effects:
Drug | Common Side Effects |
Diphenhydramine | Drowsiness, dizziness |
Chlorpheniramine | Dry mouth, sedation |
Brompheniramine | Fatigue, impaired coordination |
Consulting a healthcare provider is important. They can suggest alternative treatments. This can reduce the risk of falls while managing allergy symptoms effectively.
Second-generation
Second-generation antihistamines are designed to minimize side effects. They generally cause less drowsiness than first-generation drugs. This makes them a preferred choice for many. Here are some common second-generation antihistamines:
Loratadine (Claritin)
Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
Fexofenadine (Allegra)
These medications are less likely to impair coordination. They have a lower impact on reaction time. This makes them safer for those concerned about falls. Yet, they are not completely free of risk. Some individuals may still experience side effects. These can include mild dizziness or fatigue.
The table below outlines the differences:
Drug | Common Side Effects |
Loratadine | Mild drowsiness, headache |
Cetirizine | Fatigue, dry mouth |
Fexofenadine | Dizziness, nausea |
Choosing the right medication can reduce fall risk. It is essential to discuss options with a doctor. They can provide guidance tailored to individual needs. This ensures both safety and effective allergy management.
Alcohol Interaction
Understanding the risks linked to various drugs can be life-saving. Alcohol is one substance that significantly raises the risk of falling. It interacts with different medications, heightening their effects and compromising stability. Mixing alcohol with drugs can lead to unexpected side effects. This increases the likelihood of accidents. People who consume alcohol while on medication should be aware of these risks. Knowledge about alcohol interaction is crucial for safety.
Cumulative Effects
Drugs and alcohol can have cumulative effects. This means that their combined impact is greater than the sum of their individual effects. When alcohol interacts with medications, it can intensify their actions. This puts individuals at a higher risk of falling. Here are some ways cumulative effects manifest:
Increased dizziness: Alcohol can enhance the dizziness caused by certain medications.
Impaired coordination: Combining alcohol with drugs can worsen coordination problems.
Slower reaction times: Reaction times may significantly slow down, affecting balance.
For instance, medications like benzodiazepines and opioids are known to affect balance. When mixed with alcohol, their effects can become more pronounced. This increases the risk of falling. Being mindful of these cumulative effects is essential. It helps prevent falls and ensures safer medication use.
Professional Fall Prevention Home Care in Houston, TX - Visit Us Today
Increased Sedation
Alcohol can increase sedation when combined with certain drugs. This is especially true for medications that already have sedative properties. Increased sedation can lead to a higher risk of falls. Here are some drugs that interact with alcohol to enhance sedation:
Antidepressants: These can make individuals feel drowsy, and alcohol intensifies this effect.
Antihistamines: Often used for allergies, these can cause drowsiness when mixed with alcohol.
Sleeping pills: The primary purpose is sedation, which alcohol can magnify.
The combination of alcohol and these medications can lead to excessive drowsiness. This makes it difficult to stay alert and maintain balance. Such increased sedation can be dangerous. It heightens the risk of accidents and falls, especially in older adults. Understanding these interactions is key for safety.
Polypharmacy Risks
As people age, they often require medication to manage various health conditions. This can lead to a practice known as polypharmacy, which involves taking multiple medications simultaneously. While these drugs can help manage health issues, they also come with risks. One significant concern is the increased risk of falling. Falls can lead to severe injuries, especially in older adults. Understanding the risks associated with polypharmacy is crucial to prevent these incidents.
Multiple Prescriptions
Taking multiple prescriptions increases the risk of falling for several reasons. Each additional medication can contribute to side effects like dizziness or confusion. These side effects can make it difficult to maintain balance. The more medications a person takes, the higher the risk.
Sedatives: These can cause drowsiness and impair coordination.
Antidepressants: Some types may cause dizziness or blurred vision.
Blood pressure medications: These can lead to lightheadedness if blood pressure drops too low.
Understanding the types of medications involved is essential. Consider the following table for a clearer picture:
Medication Type | Common Side Effects |
Sedatives | Drowsiness, impaired balance |
Antidepressants | Dizziness, blurred vision |
Blood Pressure Medications | Lightheadedness, fainting |
Each medication adds to the overall risk profile. It's essential to review prescriptions regularly with healthcare providers.
Drug Interactions
Drug interactions occur when one medication affects the action of another. This can alter the effectiveness or increase side effects. Interactions can significantly increase fall risk.
Common interactions include:
Sedatives and alcohol: This combination can severely impair judgment and coordination.
Antidepressants and painkillers: Can lead to excessive sedation.
Blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs: Increase bleeding risk, which can complicate falls.
Consider how these interactions can impact daily life. For example:
An increased risk of dizziness can make walking dangerous.
Excessive sedation can lead to falls during the night.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are necessary. They can help manage and adjust medications to minimize fall risks.
Age And Sensitivity
Understanding how age affects sensitivity to medications is crucial for preventing falls. As individuals grow older, their bodies undergo changes that can alter how they process and respond to drugs. These changes can increase the likelihood of adverse side effects, such as dizziness or impaired balance, leading to a higher risk of falling. It's important to identify which medications pose the greatest threat to the elderly and tailor treatments accordingly.
Elderly Population
As people age, their bodies become less efficient in metabolizing drugs. The elderly often experience changes in body composition, including decreased muscle mass and increased fat tissue. These changes can affect how drugs are absorbed and distributed in the body. Furthermore, kidney and liver functions decline, slowing drug excretion and leading to accumulation in the system.
Common drugs that can increase the risk of falls include:
Antidepressants: These can cause drowsiness and dizziness.
Antihypertensives: Lowering blood pressure too much can lead to fainting.
Sleep aids: These often result in grogginess and impaired coordination.
The table below highlights these drugs and their potential impact:
Drug Type | Potential Impact |
Antidepressants | Drowsiness, dizziness |
Antihypertensives | Fainting, dizziness |
Sleep aids | Grogginess, impaired coordination |
Understanding these factors is vital for healthcare providers. Tailoring medication plans to reduce fall risks can significantly improve elderly patients' quality of life.
Increased Fall Risk
Drugs that affect the central nervous system can significantly heighten fall risks. Sedatives and tranquilizers, often prescribed for anxiety or sleep disorders, can lead to reduced alertness and slowed reaction times. This makes it harder to navigate environments safely.
Several factors contribute to increased fall risk:
Polypharmacy: Taking multiple medications can increase side effects.
Drug interactions: Combining certain drugs can amplify dizziness or balance issues.
Dosage errors: Incorrect doses can exacerbate adverse effects.
It's essential for caregivers and patients to be aware of these risks. Regularly reviewing medications and their side effects can help mitigate potential dangers. Discussing concerns with healthcare providers can lead to safer medication strategies, reducing fall risks and enhancing safety.
Professional Fall Prevention Home Care in Houston, TX - Visit Us Today
Preventative Measures
As we age, our bodies change. Some medications can increase the risk of falling. Understanding these risks is crucial for safety. Preventative measures can help reduce falls. By managing medications and assessing safety, we can create a safer environment. These steps are vital for maintaining independence and well-being.
Medication Review
Regular medication reviews are important. They help identify drugs that might cause falls. Consult a healthcare provider to evaluate your prescriptions. Some drugs to watch include:
Sedatives - These can make you drowsy.
Antidepressants - Some affect balance.
Blood pressure medications - They can cause dizziness.
Pain relievers - Especially opioids, which can impair movement.
Discuss any side effects with your doctor. They might adjust dosages or switch medications. Keep a list of all medications you take. Include over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Share this list with your healthcare provider during reviews.
Medication Type | Potential Effect |
Sedatives | Drowsiness |
Antidepressants | Balance issues |
Blood pressure meds | Dizziness |
Pain relievers | Impaired movement |
Safety Assessments
Conducting safety assessments in your home is essential. Identify and remove hazards that can lead to falls. Consider these steps:
Clear pathways - Ensure floors are free of clutter.
Install handrails - Place them in bathrooms and along stairways.
Improve lighting - Make sure all areas are well-lit.
Use non-slip mats - Place them in the kitchen and bathroom.
Simple changes can make a big difference. Regularly assess your living space. Ask a family member or friend to help. They might see risks you missed. Consider using assistive devices if needed. Walkers and canes provide extra support. Stay active to improve strength and balance. Exercise can reduce the risk of falls.
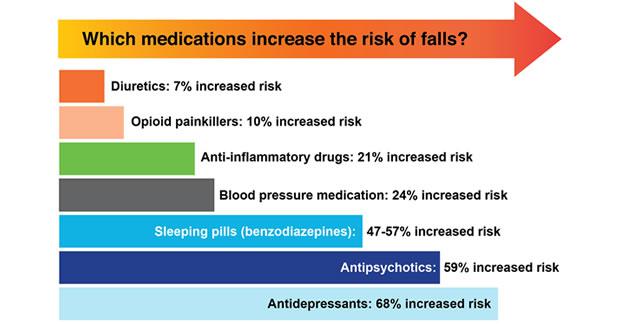
Frequently Asked Questions
What Drugs Are High Risk For Falls?
Medications like benzodiazepines, antidepressants, antipsychotics, opioids, and certain antihypertensives increase fall risk. Muscle relaxants and diuretics also contribute. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Which Home Medication Will Increase The Patient's Risk Of Falling?
Medications like sedatives, antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications can increase fall risk. Consult with your doctor to adjust dosages. Always monitor side effects and report any dizziness or instability.
What Drugs Cause Postural Drop?
Certain medications can cause postural drop, including diuretics, alpha-blockers, beta-blockers, antidepressants, and antihypertensives. Opioids and sedatives may also contribute. Always consult your healthcare provider for advice tailored to your health needs. Monitoring and adjusting medication can help manage symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding which drugs increase fall risks is crucial. Falls can lead to serious injuries. Always consult your doctor about medication side effects. Be aware of changes in your balance or coordination. Regular check-ups can help manage these risks. Lifestyle adjustments might be necessary for safety.
Consider home modifications for a fall-proof environment. Stay informed and proactive in your health decisions. Discuss concerns with healthcare providers. Knowledge empowers you to make safer choices. Prioritize safety to maintain a healthy and active lifestyle.
